Table of Contents
- 1 Key Takeaways:
- 2 What Is Self-Sovereign Identity (SSI)?
- 3 What Are the Security Risks of Centralized Identity Systems?
- 4 How Does Self-Sovereign Identity Improve Online Security?
- 5 What Are Three Pillars of Self-Sovereign Identity (SSI)?
- 6 1. Decentralized Identifiers (DIDs)
- 7 2. Verifiable Credentials (VCs)
- 8 3. Blockchain
- 9 What Are the Advantages of Self-Sovereign Identity for Individuals, Organizations, and Developers?
- 10 What Are the Three Pillars of Self-Sovereign Identity (SSI)?
- 11 How to Manage Self-Sovereign Identity with Digital ID Wallets
- 12 What Are the 10 Principles of Self-Sovereign Identity (SSI)?
- 13 What Is the Future of Self-Sovereign Identity in the Identity Ecosystem?
- 14 Identity.com
Key Takeaways:
- Self-sovereign identity (SSI) is a digital identity model that gives individuals full control and ownership over their personal data. This eliminates the reliance on centralized authorities or intermediaries to store and manage one’s data.
- With SSI, users can manage, share, and verify their identity while sharing only the minimum necessary information, ensuring privacy and reducing the risk of identity theft or unauthorized data access.
- By using secure and verifiable digital credentials, SSI helps minimize the risk of identity fraud or misuse of personal information.
You might think you’re in control of your online identity, but major corporations like Google and Facebook often have access to your personal data, such as your name, email address, and even your location. These companies store this information on their centralized servers and can use it for their own purposes. This highlights a significant flaw in current online identity systems, where businesses maintain control over your data.
Self-Sovereign Identity (SSI) offers an alternative approach, giving individuals full control over their personal digital information, reducing dependence on big tech companies, and shifting power back to users.
What Is Self-Sovereign Identity (SSI)?
Self-sovereign identity (SSI) is a digital identity model that gives individuals full control over their personal data without relying on a central authority. Unlike traditional identity systems, where organizations and companies control and manage your personal information, SSI allows you to securely store and manage your identity credentials on your own device. This decentralized approach ensures that you, and only you, decide when, how, and with whom to share your information.
SSI leverages technologies like blockchain and decentralized identifiers (DIDs) to create a secure, tamper-proof system for identity management. With SSI, your credentials—such as digital versions of your driver’s license, passport, or professional certifications—are stored in a digital wallet, encrypted, and protected by advanced cryptographic methods.
One of the key benefits of SSI is its ability to minimize the risks of data breaches and identity theft. Since your data is not stored in a centralized database, hackers have no single target to exploit. Instead, you have full autonomy over your personal information, sharing only the specific data required for a particular transaction or verification process. This selective disclosure feature of SSI enhances your privacy and security, allowing you to engage with websites, services, and organizations without exposing unnecessary personal details.
What Are the Security Risks of Centralized Identity Systems?
Self-sovereign identity (SSI) is crucial for online security because it addresses the vulnerabilities and inefficiencies of current centralized data storage and credential verification systems. These centralized systems are highly susceptible to cyberattacks and can be unreliable when critical verifications are required. Additionally, the credential verification process in these systems is often time-consuming, leading to an increase in fraudulent IDs and unchecked certifications.
Recent statistics further underscore these risks. In 2023, it was reported that the average cost of a data breach rose to $4.45 million, the highest in almost two decades, with a significant portion of these breaches involving the compromise of personal identifiable information (PII) stored in centralized databases. Moreover, a separate report revealed that over 52% of all data breaches globally involved the exposure of customer PII, leading to substantial financial and reputational damage for organizations.
How Does Self-Sovereign Identity Improve Online Security?
Self-sovereign identity improves online security by giving users control over their own identities, eliminating the need for centralized databases that can be hacked or become inaccessible. With SSI, users store their credentials securely in their digital ID wallets, and verifications are done directly and cryptographically, reducing the risk of fake credentials circulating undetected. This decentralized approach not only protects against cyberattacks but also ensures that credential verification is quick, reliable, and independent of internet connectivity or central server availability.
By moving beyond simply restoring data control to users, SSI fundamentally transforms the security landscape, making online interactions safer and more trustworthy.
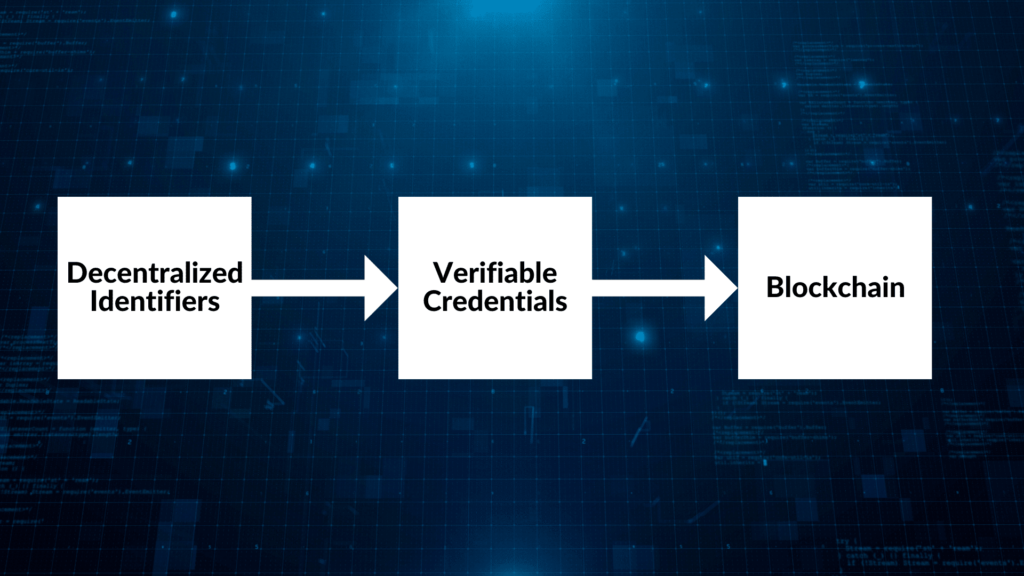
What Are Three Pillars of Self-Sovereign Identity (SSI)?
Digital identity includes all traceable data or internet footprints associated with an individual or entity. While centralized identity management allows easy tracing of data, SSI uses users’ information in unrelated patterns, enhancing privacy.
The three pillars of Self-Sovereign Identity (SSI) actively contribute to creating fraud-proof digital identities and credentials: Decentralized Identifiers (DIDs), Verifiable Credentials (VCs), and Blockchain technology.
1. Decentralized Identifiers (DIDs)
Decentralized Identifiers (DIDs) are globally unique identifiers built on decentralized databases. Unlike traditional identifiers that rely on centralized databases, DIDs operate on the decentralized blockchain framework, eliminating the need for a central authority. This allows individual identification and verification on the blockchain.
DIDs are based on encryption and decryption technology, making them cryptographically verifiable. They do not contain any personally identifiable information (PII), enhancing privacy and security. DIDs are created, owned, and controlled by users, independent of any organization. To explore more about DIDs, check out this extensive article on Decentralized Identifiers (DIDs).
2. Verifiable Credentials (VCs)
Verifiable Credentials (VCs) offer a secure and tamper-evident means of digital credential presentation. VCs rely on digital signatures to ensure validity and authenticity, making them highly secure against forgery.
VCs can be presented to organizations or verifiers as a new form of digital credential. Their validity and authenticity can be verified directly from the issuer within seconds, making them highly efficient. The “trust triangle” of verifiable credentials involves the holder, issuer, and verifier, all playing a critical role in ensuring security and authenticity. For more details on VCs, see this extensive article on verifiable credentials (VCs).
3. Blockchain
Blockchain technology closely connects verifiable credentials and decentralized identifiers, making SSI secure, private, and accessible anywhere and anytime. Blockchain is a decentralized database or ledger shared across a network of computers, known as a blockchain network. Each computer within the network, or node, collectively forms a network that records information in a decentralized manner.
The blockchain system’s design makes it impossible to alter data stored on a blockchain, providing high security. Information on the blockchain is stored in blocks, each containing a cryptographic hash of the previous block, a timestamp, and transaction data. This chain of blocks ensures that the data is immutable and cannot be altered. Blockchain technology forms the foundation for SSI, making it an optimal solution for identity management. For further reading on blockchain technology, refer to this detailed article.
What Are the Advantages of Self-Sovereign Identity for Individuals, Organizations, and Developers?
Self-sovereign identity offers numerous benefits, enhancing privacy, security, and efficiency for individuals, organizations, and developers. Individuals gain control over their data, organizations streamline credential issuance and verification, and developers create seamless, secure user experiences.
Individuals:
- Enhanced Privacy: Users own their data and decide who can access it, reducing reliance on centralized servers.
- Control & Autonomy: Users manage their digital identities, selectively sharing information.
- Convenient Digital Wallets: Securely store and manage credentials on personal devices, eliminating the need for multiple passwords.
- Revocation of Access: Users can revoke data access at any time, effectively managing their online presence.
Organizations:
- Streamlined Credential Issuance: Organizations can issue credentials quickly and cost-effectively.
- Improved Verification Efficiency: Instant and accurate identity verification eliminates the need for manual checks.
- Enhanced Security: Advanced cryptography ensures credential authenticity, reducing fraud.
- Continued Verification: Credentials remain valid even if the issuer goes offline.
Developers:
- Seamless User Experience: Create passwordless, user-friendly experiences through SSI-powered wallets.
- Strong Authentication: Provide a secure alternative to complex authentication methods.
- Selective Disclosure: Allow users to share only essential information, protecting sensitive data.
- Direct Data Exchange: Enable peer-to-peer data exchange, enhancing privacy and security by removing intermediaries.
What Are the Three Pillars of Self-Sovereign Identity (SSI)?
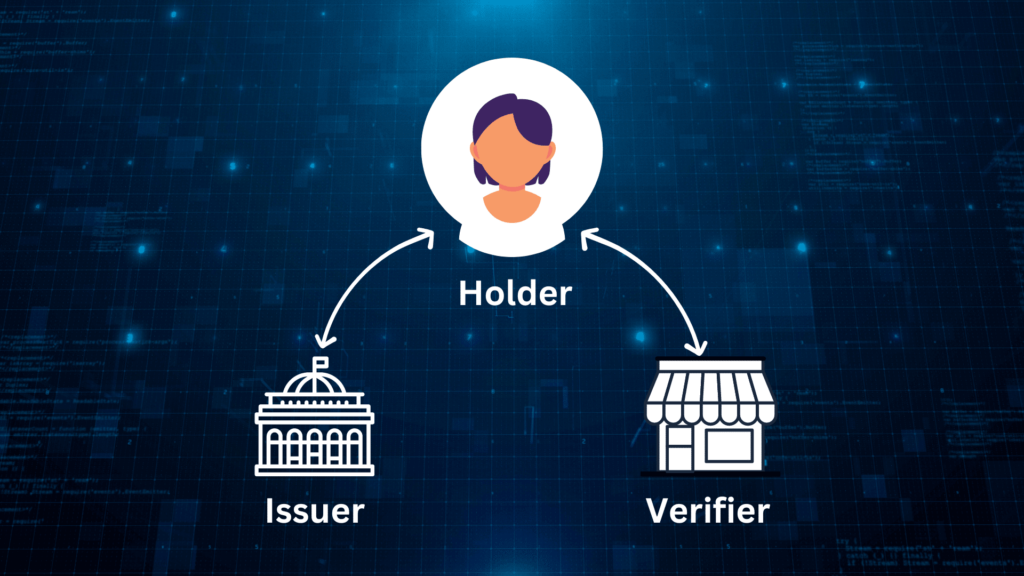
Self-Sovereign Identity (SSI) relies on a collaborative ecosystem to establish trust and validate digital credentials. This system mirrors traditional credential issuance, such as a university issuing a degree that a student presents to a potential employer. However, SSI offers enhanced privacy and security. In SSI, this three-way interaction is known as the Trust Triangle, consisting of the issuer, holder, and verifier.
1. The Issuer
The issuer, often an organization or accredited individual, is responsible for creating and issuing verifiable credentials. Examples include universities, healthcare providers, governments, and banks. Their role is to validate and securely issue credentials to individuals.
2. The Holder
The holder is the individual who possesses and manages their verifiable credentials. They have complete control over their data, deciding when and how to share it. Holders can selectively disclose specific credential information to different verifiers, ensuring privacy control.
3. The Verifier
Verifiers are entities or organizations that request and validate the credentials presented by the holder. They rely on this information to make informed decisions, like granting access to services or benefits. Verifiers can easily confirm the authenticity and validity of credentials by directly interacting with the issuer, eliminating manual checks and intermediaries.
How to Manage Self-Sovereign Identity with Digital ID Wallets
Digital ID wallets are essential tools for seamlessly managing digital identities and verifiable credentials. They provide secure, decentralized storage for credentials, guaranteeing integrity and accessibility. Unlike traditional methods that rely on email or downloads, digital ID wallets securely store credentials on users’ devices.
These wallets also streamline access to credentials. Users can easily share required information directly from their digital ID wallet when verifiers request proof of identity or specific credentials. This eliminates the need for multiple passwords or physical documents, simplifying identification and verification processes while empowering individuals to manage their self-sovereign identity effectively.
What Are the 10 Principles of Self-Sovereign Identity (SSI)?
In 2016, Christopher Allen introduced ten critical principles that underpin any effective SSI system. These principles guide the development and implementation of secure and trustworthy SSI solutions.
1. Existence: Digital identities must be grounded in reality, connecting to a verifiable physical entity or individual.
2. User Control: Individuals have the ultimate authority over their digital identities.
3. Unrestricted Access: Users should always have unrestricted access to their own identity data.
4. Transparency by Design: The operations and management of SSI systems should be transparent and open for scrutiny.
5. Persistence for Life: Digital identities should be long-lasting, allowing individuals to maintain them over time.
6. Portable Identities: Users should be able to effortlessly transfer their credentials and data between different SSI providers.
7. Interoperable Systems: SSI systems should be designed for interoperability across various platforms and gain international recognition.
8. Consent is Key: Obtaining user consent before sharing and utilizing identity information is crucial.
9. Data Minimization: Individuals should only disclose essential data in specific situations.
10. User Data Protection:Users’ rights to their identity data should always be protected.
What Is the Future of Self-Sovereign Identity in the Identity Ecosystem?
The future of identity management is shifting towards individual control with Self-Sovereign Identity (SSI). Unlike the centralized data models of Web 2.0, where users’ personal information is often controlled by large corporations, SSI empowers individuals to own and manage their digital identities independently. This shift represents a significant departure from traditional data collection methods, potentially transforming business models that rely heavily on user data.
As the market for SSI solutions continues to grow, with projections suggesting it could become a trillion-dollar industry, it is set to become a major player in the identity ecosystem. While this shift may present challenges for established tech giants, it offers the promise of a more secure, private, and user-centric digital environment.
Identity.com
The SSI approach to identity management aligns with what Identity.com represents. One of our pursuits is a user-centric internet, where users have control over their data. More reason why Identity.com doesn’t take the back seat in contributing to this future via identity management systems and protocols. We also belong to the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C), the standards body for the World Wide Web.
The work of Identity.com as a future-oriented company is helping many businesses by giving their customers a hassle-free identity verification process. Identity.com is an open-source ecosystem providing access to on-chain and secure identity verification. Our solutions improve the user experience and reduce onboarding friction through reusable and interoperable Gateway Passes. Please get in touch or visit our FAQs page for more info about how we can help you with identity verification and general KYC processes.